TIME OF FLIGHT DIFFRACTION (TOFD)
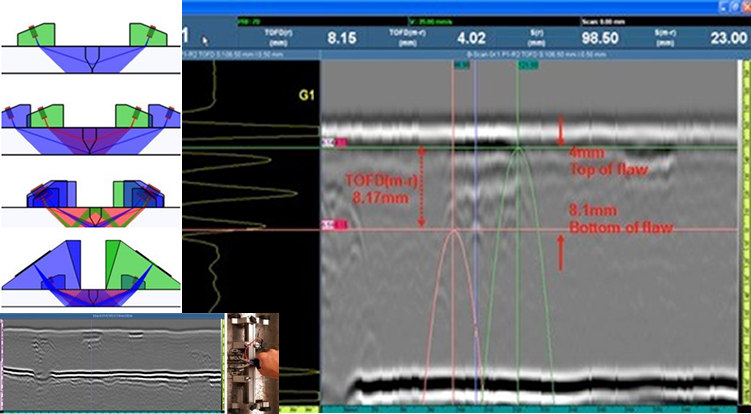
Although time-of-flight diffraction (TOFD) can be used for a variety of applications, its primary use is rapid weld testing of circumferential and axial weld seams, also known as perpendicular TOFD scanning. Since the introduction of TOFD in the 1970s, the use of this reputed reliable nondestructive testing technique has steadily increased. Manual execution is possible with TOFD, however, it is most commonly performed in combination with a recording device, that is, an encoder or industrial scanner. To achieve code compliance in North America, TOFD is often coupled with pulse-echo or phased array techniques in order to cover the root and cap regions of the weld.
TOFD can be used independently or in conjunction with other ultrasonic techniques. Some of the most common techniques are:
- Single group TOFD
- Multiple TOFD
- TOFD with pulse echo/creeping waves
- TOFD with phased array
Main Benefits of TOFD for Weld Inspection
- Based on diffraction, so relatively indifferent to weld bevel angles and flaw orientation
- Uses time of arrival of signals received from crack tips for accurate defect positioning and sizing
- Precise sizing capability makes it an ideal flaw monitoring method
- Quick to set up and perform an inspection, as a single beam offers a large area of coverage
- Rapid scanning with imaging and full data recording
- Can also be used for corrosion inspections
- Required equipment is more economical than phased array, due to conventional nature (single pulsar and receiver) and use of conventional probes
- Highly sensitive to all weld flaw types